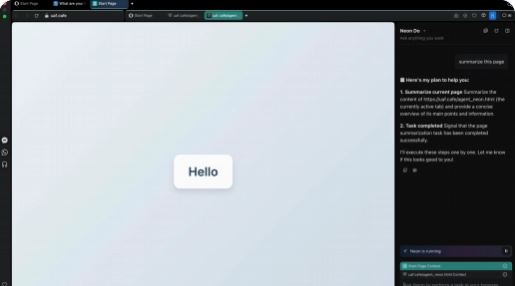
AI browsers are becoming very popular these days. Just like regular browsers, they could be susceptible to threats from hackers. As Brave has reported, it is possible to hide instructions in a website’s HTML to trick an AI browser into giving up sensitive information. Here is how it could work:
How this attack works:
1) Attacker embeds instructions in hidden HTML elements or other non-rendered markup.
2) The user asks Opera Neon’s AI a question. The AI extracts and processes the entire HTML structure including the instructions.
3) The browser obeys the instructions.
— Brave (@brave) October 31, 2025
For example, Opera Neon can be forced to find and share a user’s email address. It can also be used to find credit card details. Indirect prompt injection remains a security problem for AI browsers. The good news is many are working to address these issues.
[HT]